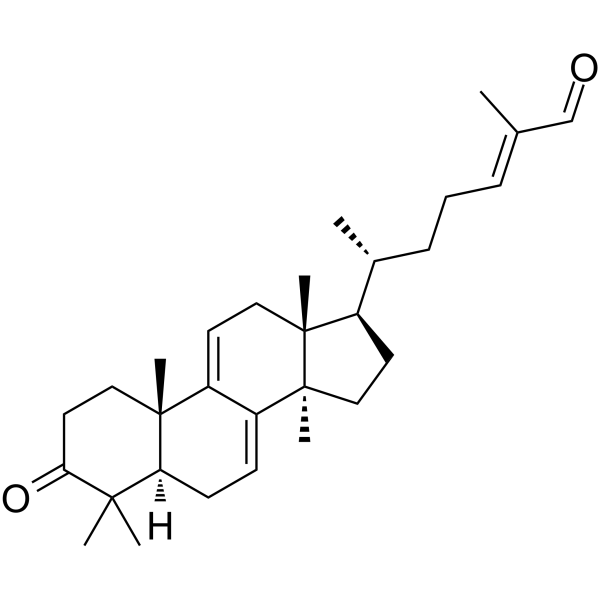
Ganoderal A
CAS No. 104700-98-3
Ganoderal A( —— )
Catalog No. M31131 CAS No. 104700-98-3
The oxygenated sterols( 26-oxygenosterols ganoderol A, ganoderol B, ganoderal A, and ganoderic acid Y) from G. lucidum can inhibit cholesterol biosynthesis via conversion of acetate or mevalonate as a precursor of cholesterol.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 360 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameGanoderal A
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionThe oxygenated sterols( 26-oxygenosterols ganoderol A, ganoderol B, ganoderal A, and ganoderic acid Y) from G. lucidum can inhibit cholesterol biosynthesis via conversion of acetate or mevalonate as a precursor of cholesterol.
-
DescriptionThe oxygenated sterols( 26-oxygenosterols ganoderol A, ganoderol B, ganoderal A, and ganoderic acid Y) from G. lucidum can inhibit cholesterol biosynthesis via conversion of acetate or mevalonate as a precursor of cholesterol.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number104700-98-3
-
Formula Weight436.68
-
Molecular FormulaC30H44O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 5.26 mg/mL (12.05 mM)
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Apiin
Apiin has inhibitory activity in-vitro on iNOS expression and nitrite production when added before LPS stimulation in the medium of J774.A1 cells.
-
Deferoxamine mesylat...
An iron chelator that binds iron and aluminium; increases HIF-1α transactivation in diabetes by preventing iron-catalyzed reactive oxygen stress.
-
Malonic acid
Malonic acid (propanedioic acid) is the archetypal example of a competitive inhibitor: it acts against succinate dehydrogenase (complex II) in the respiratory electron transport chain. Malonic acid is found to be associated with malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency which is an inborn error of metabolism.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


